Millwrights are the cornerstone of industries that rely on heavy machinery and equipment. They are skilled craftsmen who install, dismantle, repair, reassemble, and move machinery in factories, power plants, and construction sites. Their role is integral in maintaining the heartbeat of many industrial operations.
Millwright skills cover a broad spectrum, including mechanical knowledge, precision, and attention to detail, as well as soft skills like teamwork and communication. Assessing these abilities requires a comprehensive understanding of both the technical and interpersonal demands of the job.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Millwright skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 7 essential Millwright skills, 6 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
7 fundamental Millwright skills and traits
The best skills for Millwrights include Mechanical Aptitude, Blueprint Reading, Precision Alignment, Welding Techniques, Rigging Knowledge, Problem Solving and Hydraulics Understanding.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 7 essential skills of a Millwright.
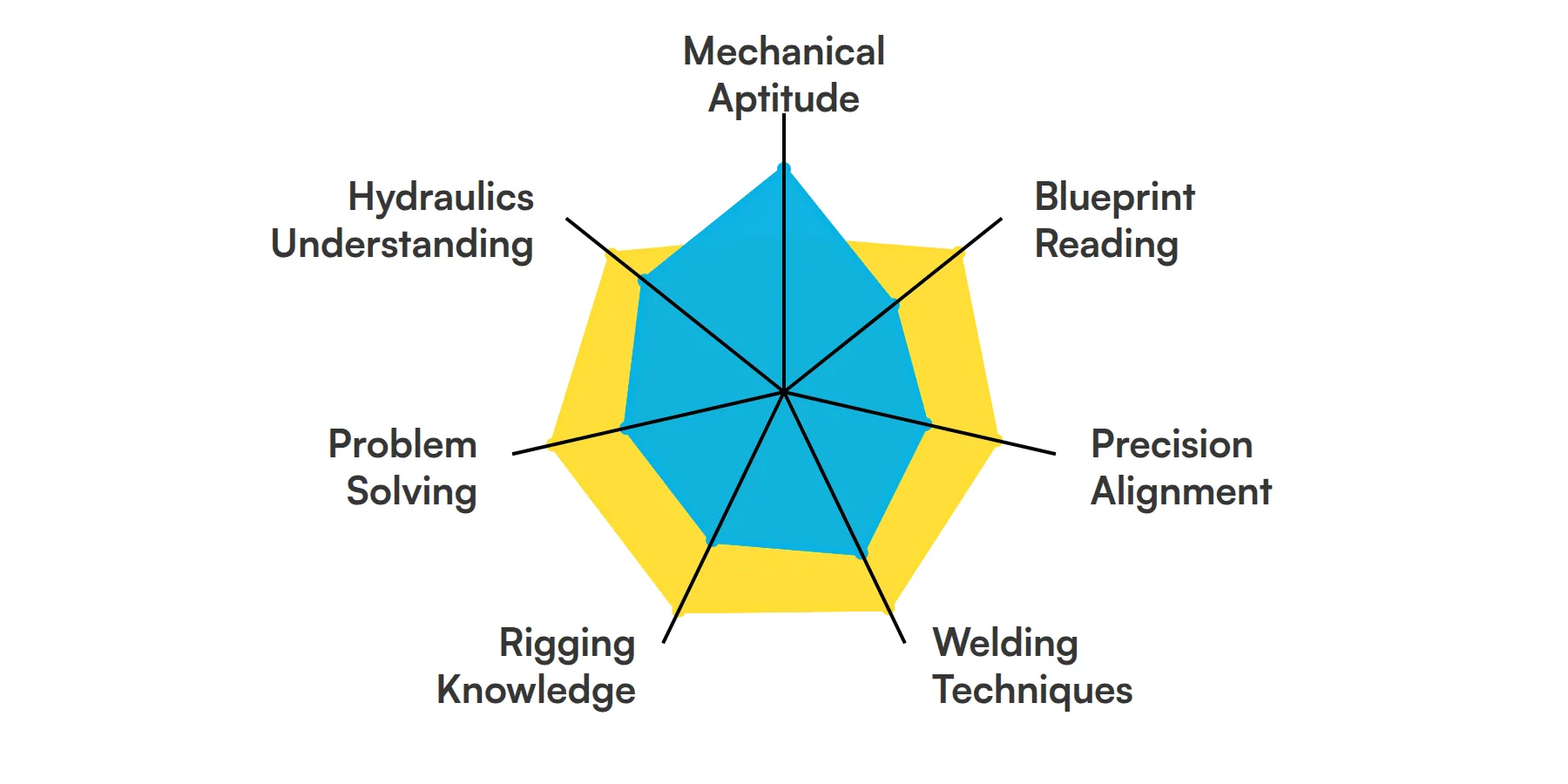
Mechanical Aptitude
A millwright's primary role involves working with machinery and equipment, which means having a strong mechanical aptitude is crucial. This skill allows them to understand the mechanics of different machines, diagnose issues, and perform maintenance or repairs effectively to ensure smooth operation.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Millwright Job Description.
Blueprint Reading
Reading and understanding blueprints is key for millwrights as they frequently work with intricate machine layouts and assembly schematics. This skill enables them to accurately interpret design specifications and ensure that machinery is set up and maintained according to detailed plans.
Precision Alignment
In the role of a millwright, precision is everything. Precision alignment skills are used to ensure that components are correctly placed and machinery operates without error, minimizing wear and tear and maximizing operational efficiency.
Welding Techniques
Welding is a vital component of many millwright tasks. This skill helps millwrights join metal pieces, repair structures, or modify equipment as needed. A good grasp of different welding techniques ensures that their work is durable and reliable.
Rigging Knowledge
Rigging involves the art of lifting and moving heavy objects safely. Millwrights utilize this skill to position heavy machinery during installation or repairs, ensuring that tasks are completed without incident and with optimal safety.
Problem Solving
A millwright often encounters unexpected challenges when working with complex machinery. Problem-solving skills empower them to identify the root of issues quickly and craft practical solutions, minimizing downtime and keeping operations running smoothly.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Hydraulics Understanding
Many machines depend on hydraulic systems to function, so millwrights need a clear understanding of how these systems work. This skill allows them to troubleshoot, repair, and maintain hydraulic equipment effectively.
6 secondary Millwright skills and traits
The best skills for Millwrights include Electrical Knowledge, Fabrication Skills, Safety Compliance, Computer Literacy, Analytical Thinking and Tool Proficiency.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 6 secondary skills of a Millwright.
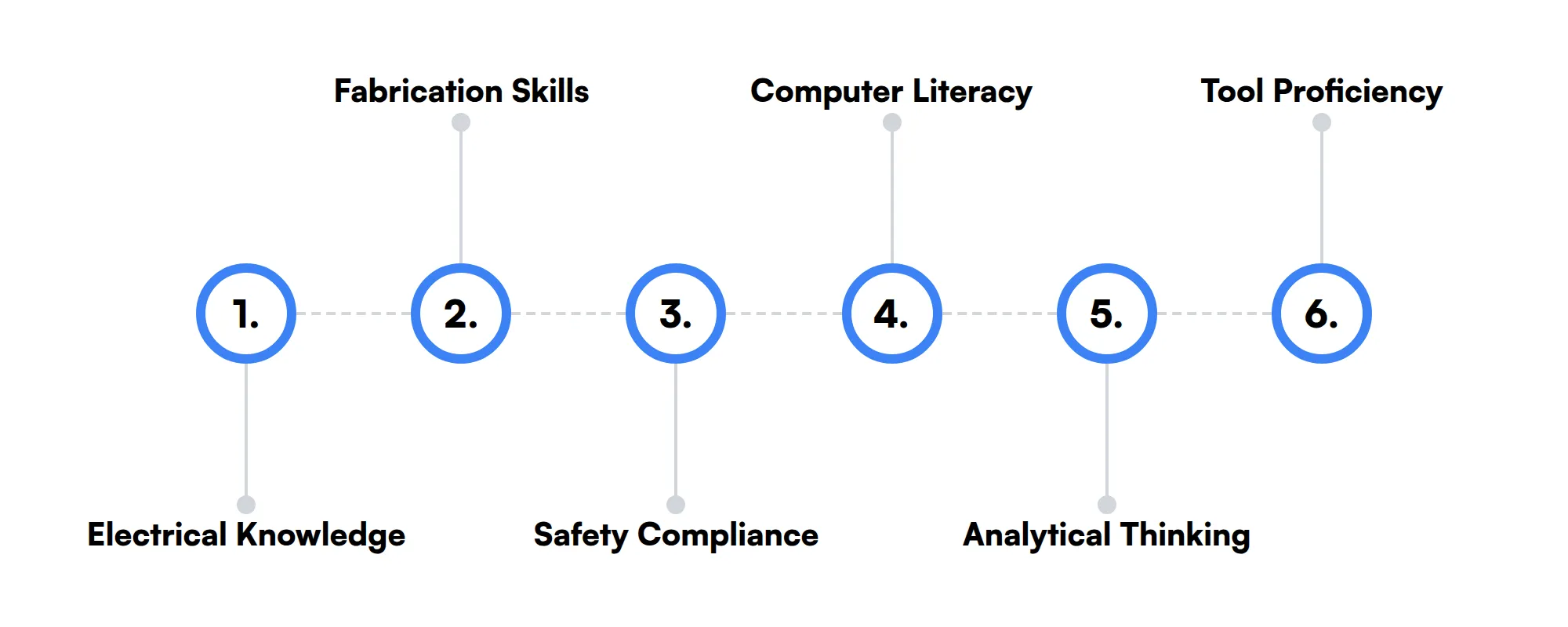
Electrical Knowledge
While not the main focus, understanding electrical systems helps millwrights to collaborate effectively with electricians and perform minor electrical repairs when necessary.
Fabrication Skills
Being able to fabricate parts or structures allows millwrights to customize or repair equipment on-site, which can be cost-effective and time-saving in the long run.
Safety Compliance
Adhering to safety regulations and standards protects not only the millwright but also others working around them. Knowledge of safety practices is fundamental to preventing workplace accidents.
Computer Literacy
As technology advances, some machinery includes computerized control systems. Basic computer skills enable millwrights to operate, adjust, and troubleshoot these modern systems.
Analytical Thinking
This skill aids millwrights in assessing situations thoroughly, interpreting data or patterns, and making informed decisions about equipment maintenance or interventions.
Tool Proficiency
With a wide array of tools at their disposal, millwrights must be proficient in selecting and using the right tools for each task. This proficiency can greatly impact the efficiency and quality of their work.
How to assess Millwright skills and traits
Assessing the skills of a Millwright goes beyond merely checking qualifications on paper. Understanding a candidate's mechanical aptitude, blueprint reading ability, and precision alignment skills can be challenging through resumes alone. It's important to delve deeper into their proficiency in welding techniques, rigging knowledge, and how adept they are at problem-solving, especially with complex hydraulic systems.
To confidently evaluate these competencies, skills-based assessments become crucial tools. Instead of relying solely on traditional resumes, consider utilizing assessments that simulate the real-world tasks Millwrights handle daily. Adaface assessments are designed to help you achieve 2x improved quality of hires and an 85% reduction in screening time, by providing insights into a candidate's problem-solving abilities and technical acumen. This approach ensures candidates possess not only theoretical knowledge but also practical expertise in the specific skills your operation requires.
Let’s look at how to assess Millwright skills with these 2 talent assessments.
Millwright Test
Millwright Test evaluates proficiency in mechanical systems and machinery maintenance with scenario-based MCQ questions.
Candidates are assessed on their expertise in precision measurement, understanding of mechanical tools, and capability in blueprint reading. They must also demonstrate knowledge of preventive maintenance and the use of hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
High performers exhibit strong mechanical aptitude and meticulous attention to detail, crucial for dealing with rigging and hoisting tasks. Knowledge of safety protocols is also evaluated.
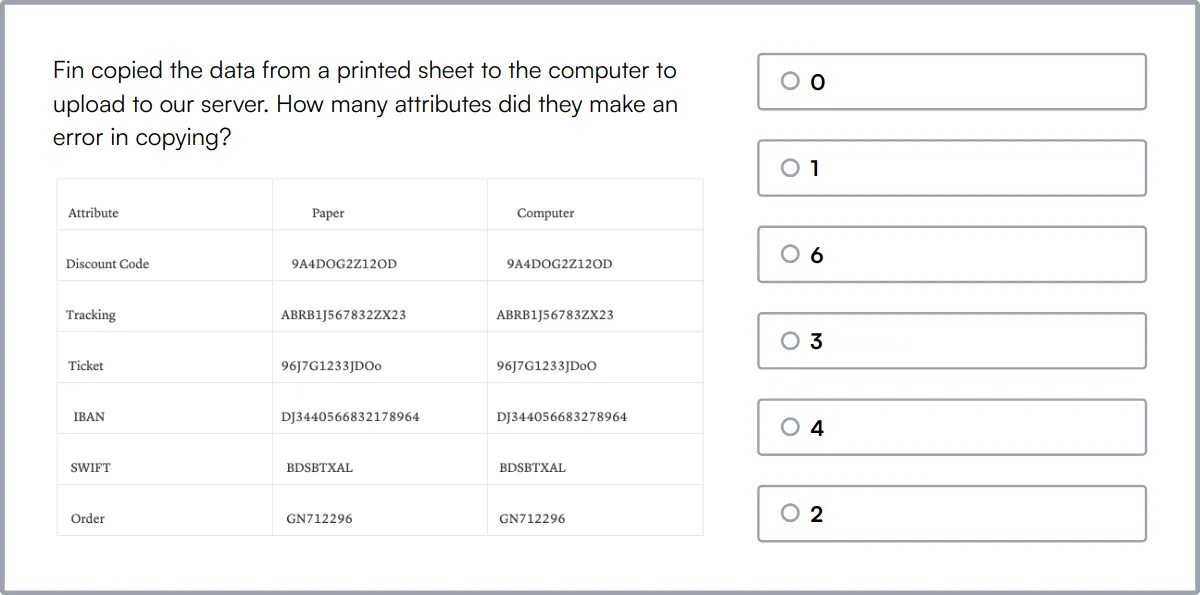
Problem Solving Test
Problem Solving Test measures a candidate’s ability to process instructions, analyze data, and tackle complex problems or scenarios.
The test evaluates skills in abstract reasoning, critical thinking, and deductive reasoning. Participants must navigate tasks requiring inductive reasoning and pattern matching, complemented by spatial reasoning capabilities.
Candidates who do well demonstrate strong problem-solving abilities and exhibit agile learning capability. These skills are directly related to improving coachability and learning agility.
Summary: The 7 key Millwright skills and how to test for them
| Millwright skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Mechanical Aptitude | Observe the ability to understand and manipulate mechanical systems. |
| 2. Blueprint Reading | Evaluate comprehension of technical drawings and ability to interpret plans. |
| 3. Precision Alignment | Assess skill in achieving exact positioning of machinery components. |
| 4. Welding Techniques | Check proficiency in fusing materials and handling welding equipment. |
| 5. Rigging Knowledge | Test understanding of load handling and rigging equipment use. |
| 6. Problem Solving | Determine capability to identify and resolve mechanical issues. |
| 7. Hydraulics Understanding | Measure comprehension of fluid systems and hydraulic mechanisms. |
Millwright Test
Millwright skills FAQs
How can you assess a millwright's mechanical aptitude?
To assess mechanical aptitude, consider a hands-on test with real machinery, or use aptitude tests that simulate mechanical scenarios. Interviews focusing on past experience with different mechanical systems can also help.
What are effective ways to evaluate blueprint reading skills?
Give candidates blueprints to analyze, interpret, and discuss their understanding of the specifications. Practical tests involving the creation or assembly of structures based on blueprints can also be insightful.
How do you test a millwright’s precision alignment ability?
Use alignment tools such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems in a practical test. Ask candidates to align machinery components and evaluate their accuracy and attention to detail.
Why is rigging knowledge important for millwrights, and how can you assess it?
Rigging knowledge ensures safe handling of heavy machinery. Assess this skill with situational questions about load calculations and secure lifting methods, and observe candidates during a rigging task.
What methods can verify a candidate's welding techniques?
Practical welding tests can showcase a candidate’s skill level. Evaluate their technique, understanding of different welding types, and inspection of completed welds for quality and safety.
How important is safety compliance and how can it be evaluated in millwrights?
Safety compliance prevents accidents and ensures a safe working environment. Assess candidates’ knowledge of safety regulations and protocols through interviews or safety scenario tests.
How do you gauge a millwright's computer literacy?
Evaluate their proficiency with maintenance management systems (CMMS) or any relevant software by asking practical questions or conducting a test to use these systems for everyday millwright tasks.
What’s the best approach to test problem-solving skills in millwright candidates?
Use practical scenarios that require diagnosing and resolving equipment issues. Discuss their problem-solving thought processes and ask how they handled previous mechanical challenges.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



