IT specialists are the backbone of any organization's technology infrastructure. They ensure that all systems, networks, and data are secure, efficient, and running smoothly, enabling the business to operate without technical interruptions.
The skills required for an IT specialist include a deep understanding of network management, cybersecurity, and system administration. Additionally, they must possess strong analytical abilities and effective communication skills to troubleshoot issues and collaborate with other team members.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job IT Specialist skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 8 essential IT Specialist skills, 10 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
8 fundamental IT Specialist skills and traits
The best skills for IT Specialists include Technical Proficiency, Network Management, Cybersecurity Fundamentals, System Administration, Data Management, Technical Support, Cloud Computing and Problem Solving.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 8 essential skills of a IT Specialist.
Technical Proficiency
An IT Specialist must be adept with various software, hardware, and networks. This skill ensures they can manage, troubleshoot, and repair technological systems effectively, keeping business operations smooth.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Network Management
Understanding and managing networks is crucial for an IT Specialist. They need to ensure secure and efficient network performance, which includes configuring network hardware, deploying updates, and monitoring system security.
Cybersecurity Fundamentals
IT Specialists must safeguard data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This involves implementing security protocols, conducting regular system checks, and staying updated with the latest security trends and compliance regulations.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Cyber Security Analyst Job Description.
System Administration
This skill involves installing, configuring, and maintaining operating systems across a variety of work environments. IT Specialists use this skill to ensure optimal system performance and troubleshoot issues that arise.
Data Management
Effective data management is key for an IT Specialist to ensure integrity, accessibility, and security of data. They handle backups, recovery, and organize data to support business outcomes.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Technical Support
Providing end-user support is a daily responsibility for IT Specialists. They need to communicate solutions effectively, resolve technical issues, and improve user satisfaction.
Cloud Computing
With many businesses moving to the cloud, IT Specialists must be skilled in cloud services and infrastructure. They manage and support cloud applications and data storage solutions to enhance business flexibility and scalability.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Cloud Engineer Job Description.
Problem Solving
IT Specialists often face unexpected challenges. Strong problem-solving skills enable them to diagnose issues quickly and implement effective solutions, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
10 secondary IT Specialist skills and traits
The best skills for IT Specialists include Project Management, Documentation Skills, Vendor Management, Training Skills, Analytical Thinking, Adaptability, Communication Skills, Regulatory Compliance, Resource Management and Continuous Learning.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 10 secondary skills of a IT Specialist.
Project Management
Coordinating IT projects, from upgrades to system deployments, requires effective project management skills to ensure timely and within-budget delivery.
Documentation Skills
Creating and maintaining accurate documentation is necessary for system configurations, changes, and processes, aiding in compliance and knowledge transfer.
Vendor Management
IT Specialists often interact with software and hardware vendors. Effective vendor management ensures the best technological solutions and support are available for the organization.
Training Skills
They often conduct training sessions for staff on new systems and software, ensuring smooth adoption and minimizing resistance to technological changes.
Analytical Thinking
Analyzing complex data and system logs to improve system performance and predict potential issues before they become critical problems.
Adaptability
Technology evolves rapidly, and IT Specialists must adapt to new tools and processes to maintain and enhance system efficiency and security.
Communication Skills
Clear communication is essential for IT Specialists to explain technical issues and solutions to non-technical stakeholders, ensuring alignment and understanding across the organization.
Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and implementing IT policies that comply with relevant laws and regulations to avoid legal issues and maintain operational integrity.
Resource Management
Efficiently managing IT resources, including hardware, software, and human capital, to optimize performance and cost-effectiveness.
Continuous Learning
The tech field is constantly evolving, and staying informed about new technologies and methodologies is crucial for an IT Specialist's ongoing effectiveness and career growth.
How to assess IT Specialist skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of IT Specialists involves more than just glancing at their resumes. While resumes may highlight their educational background and certifications, they do not provide a clear picture of their hands-on capabilities in areas like network management, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
To truly understand whether an IT Specialist can handle the demands of your organization, practical and scenario-based assessments are key. This is where tools like Adaface come into play, offering tailored assessments that test for a range of IT skills from technical proficiency to problem solving. By using these assessments, companies have seen a 85% reduction in screening time. Learn more about these assessments here.
Moreover, evaluating an IT Specialist's ability to manage systems, secure networks, and support users requires a comprehensive approach. It's not just about knowing the tools, but how effectively they can apply their knowledge to solve real-world problems and enhance the technological framework of your business.
Let’s look at how to assess IT Specialist skills with these 6 talent assessments.
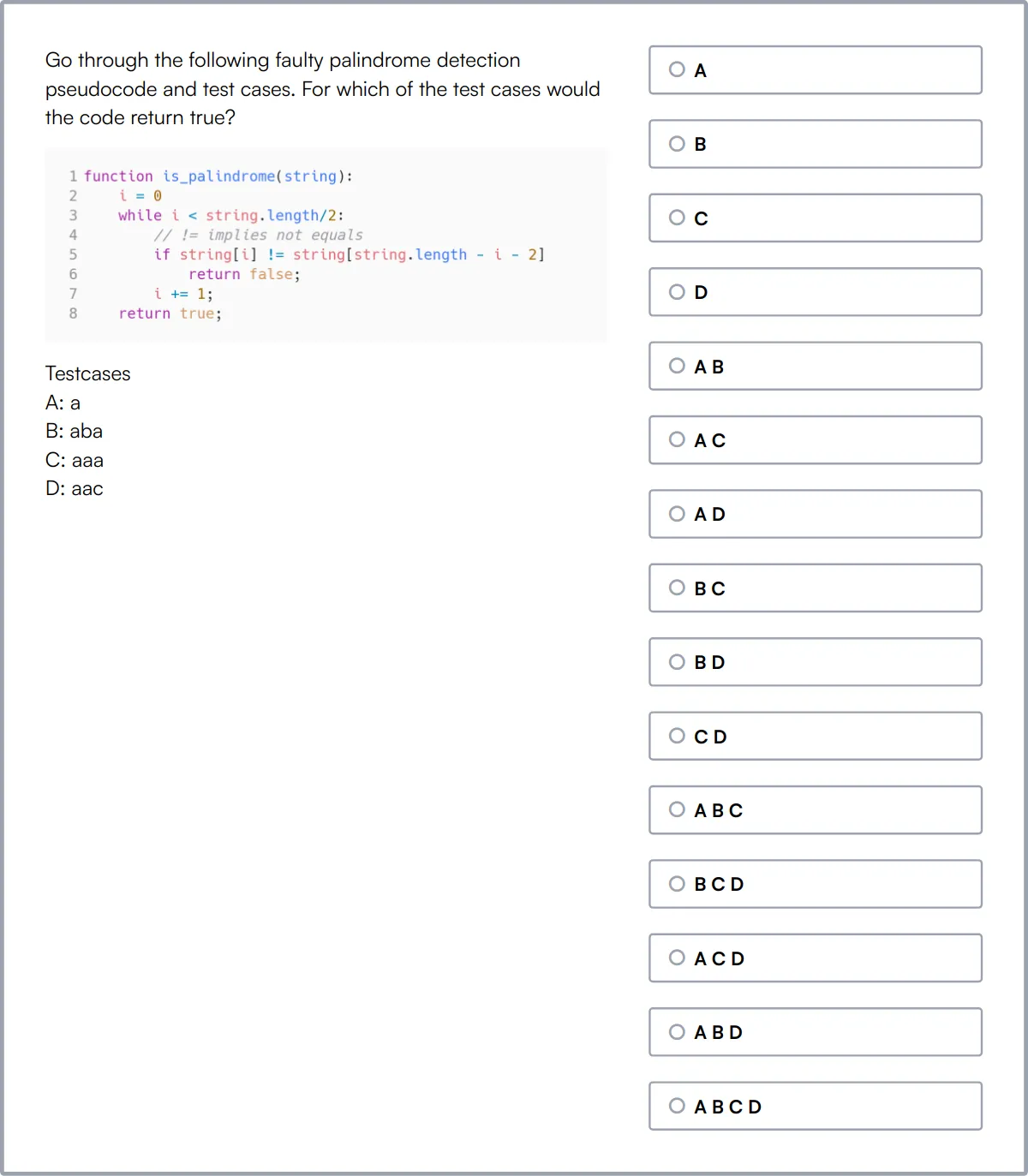
Technical Aptitude Test
Technical Aptitude Test evaluates a candidate's general technical aptitude and problem-solving skills. It covers programming fundamentals, data structures, algorithm basics, and technical aptitude.
The test assesses understanding of basic computer concepts, programming fundamentals, data structures, time complexity, database management, networking and security, system administration, web development, and software engineering. Candidates are also evaluated on their ability to apply critical thinking, logical reasoning, and analytical skills to solve complex technical problems.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong grasp of programming fundamentals, data structures, and algorithm basics. They also show proficiency in technical aptitude and problem-solving skills.
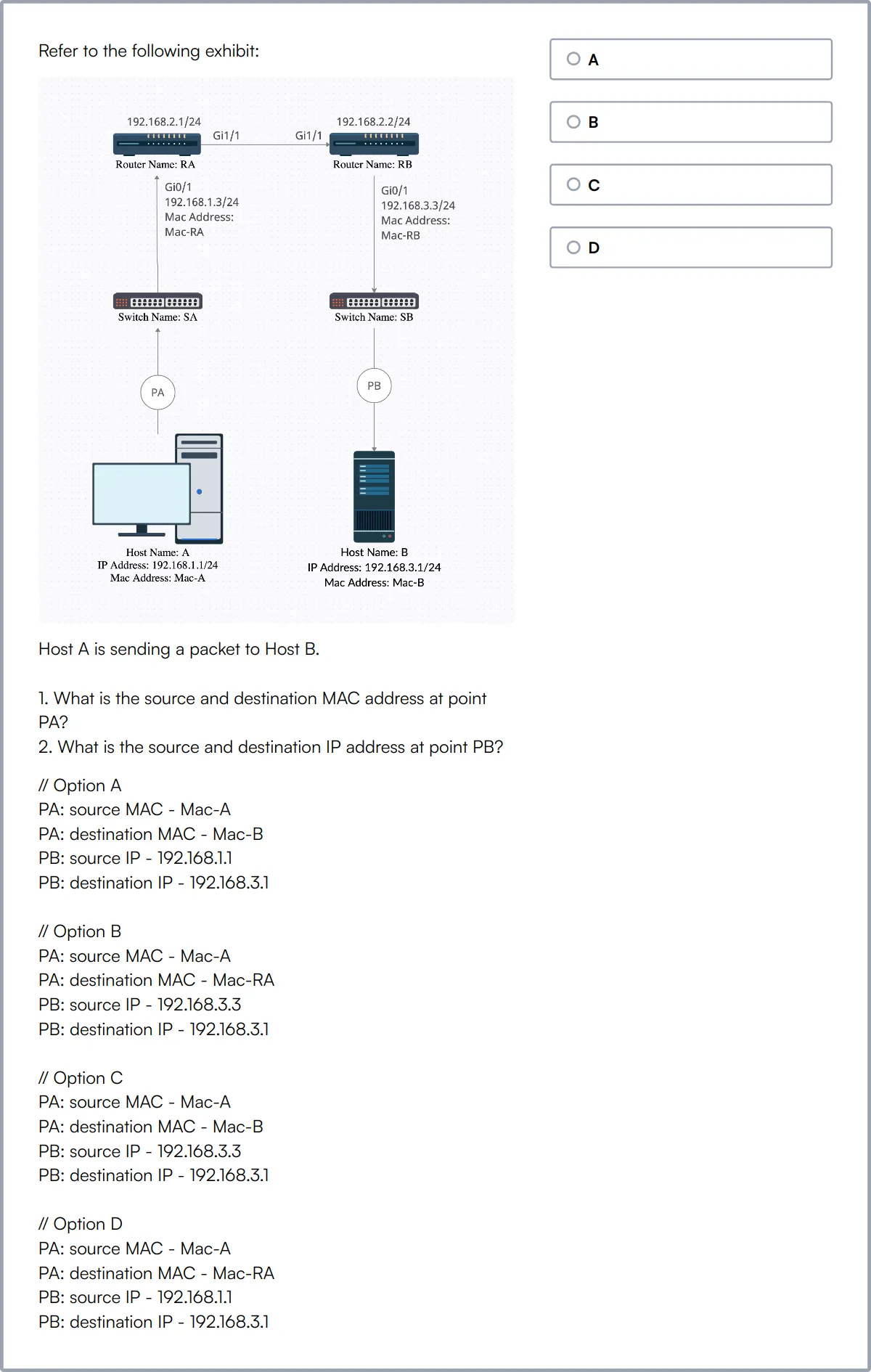
Network Engineer Online Test
Network Engineer Online Test evaluates candidates on their technical knowledge and practical skills related to computer networking. It covers network protocols, network security, routing and switching, and network troubleshooting.
The test assesses understanding of network protocols, network architecture, network security, IP addressing, subnetting, routing, switching, WAN technologies, network troubleshooting, and network management. It aims to evaluate candidates' proficiency in designing, implementing, and maintaining complex network infrastructures.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate expertise in network protocols, network security, and network troubleshooting. They also show proficiency in network design and management.
Cyber Security Assessment Test
Cyber Security Assessment Test evaluates candidates on Cyber Security basics, their ability to detect security risks, and setup guards against future cyber attacks. It covers network security, cybersecurity attacks, cryptography, and web security.
The test assesses understanding of network security protocols, cybersecurity attacks, cryptography techniques, web security, email security, malware, data security, data governance, cybersecurity defenses, risk assessments, and network tests. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to detect and mitigate security risks.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong knowledge of network security, cybersecurity attacks, and cryptography. They also show proficiency in web security and data security.
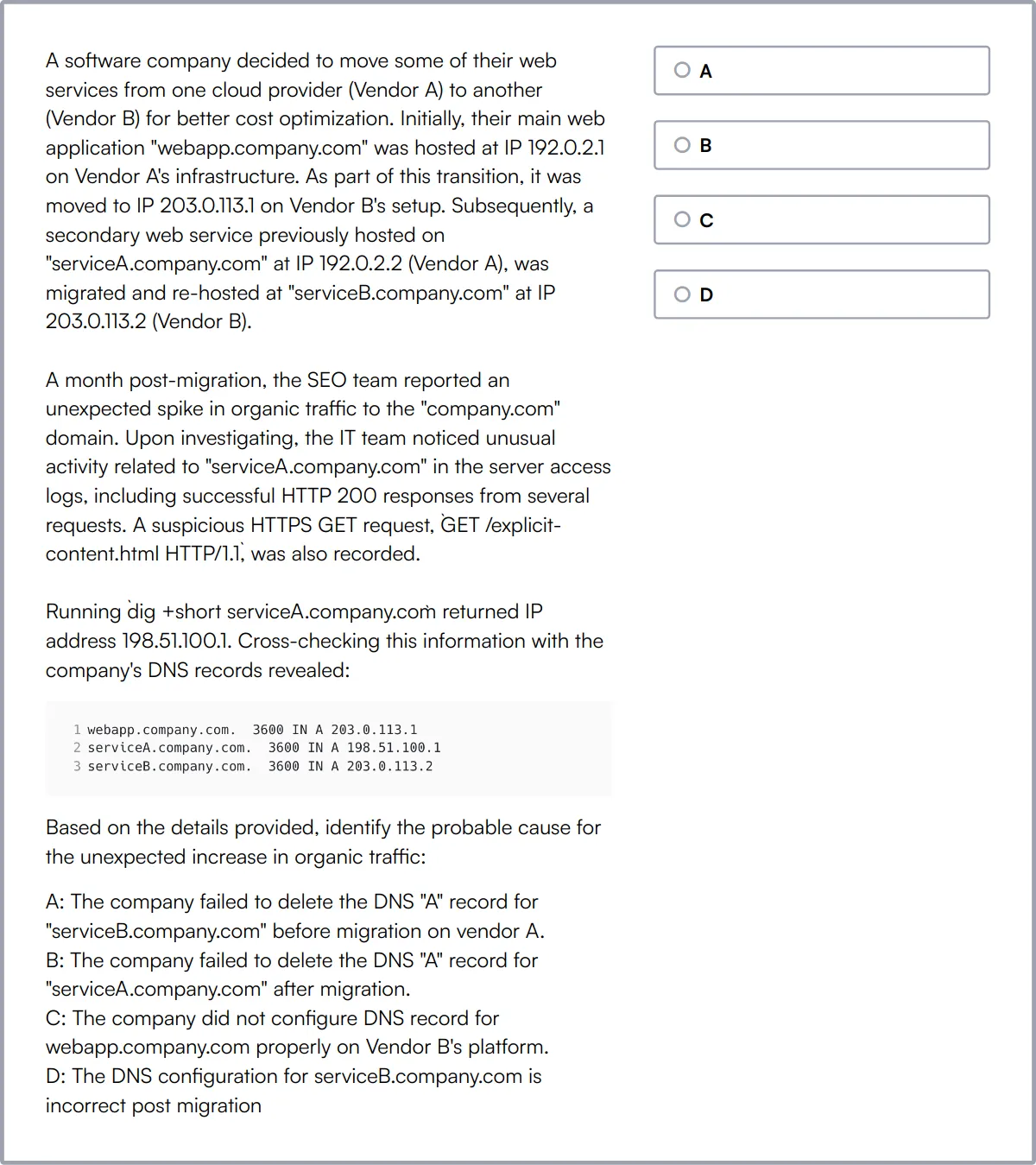
Windows System Administration Online Test
Windows System Administration Online Test evaluates candidates on their understanding of core Windows system administration concepts. It covers Windows System Administration, Active Directory, Group Policy, and Windows Server.
The test assesses understanding of Active Directory, group policy management, network services, system monitoring, scripting languages, server virtualization, and disaster recovery. It aims to evaluate the candidate's ability to manage Windows-based enterprise environments.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate expertise in Windows System Administration, Active Directory, and Group Policy. They also show proficiency in PowerShell scripting and server security.
CISCO Data Center Online Test
CISCO Data Center Online Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge and skills related to various aspects of data center operations. It covers data center networking, Cisco UCS, storage area networks, and data center security.
The test assesses understanding of data center networking, Cisco UCS, storage area networks, data center security, virtualization, network architecture, network services, data center management, data center automation, and data center troubleshooting. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to manage and troubleshoot data center operations.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong knowledge of data center networking, Cisco UCS, and storage area networks. They also show proficiency in data center security and virtualization.
Technical Support Test
Technical Support Test assesses understanding of IT infrastructure, troubleshooting, and communication skills. It covers operating system fundamentals, networking concepts, IT service protocols, and database management.
The test assesses understanding of operating systems, networking, hardware and software support, IT service protocols, scripting languages, and simulated support scenarios. It measures problem-solving abilities and customer service skills in real-world technical issues.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate strong knowledge of operating system fundamentals, networking concepts, and IT service protocols. They also show proficiency in problem-solving and customer service skills.
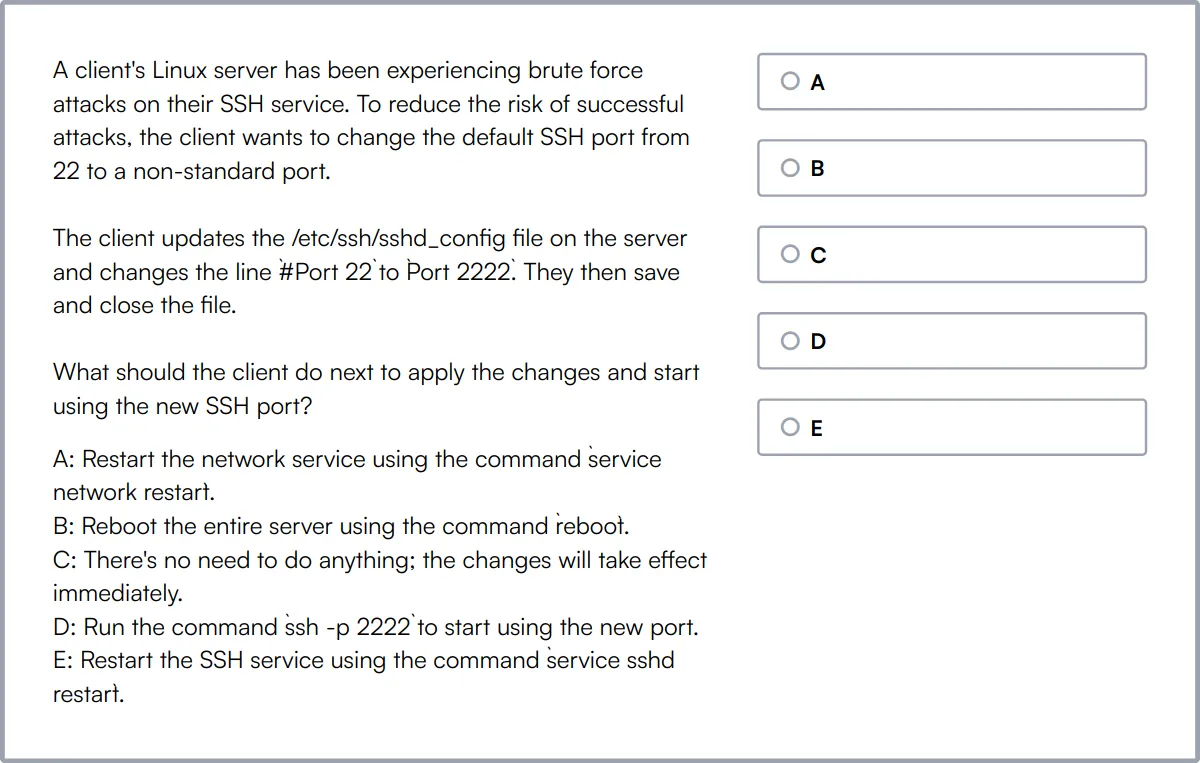
Summary: The 8 key IT Specialist skills and how to test for them
| IT Specialist skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Technical Proficiency | Evaluate knowledge of relevant software, hardware, and IT tools. |
| 2. Network Management | Assess ability to configure, maintain, and troubleshoot network systems. |
| 3. Cybersecurity Fundamentals | Check understanding of security protocols and threat mitigation. |
| 4. System Administration | Gauge skills in managing and maintaining IT infrastructure. |
| 5. Data Management | Measure ability to organize, store, and retrieve data efficiently. |
| 6. Technical Support | Evaluate problem-solving skills in assisting users with technical issues. |
| 7. Cloud Computing | Assess knowledge of cloud services and deployment strategies. |
| 8. Problem Solving | Determine ability to identify and resolve IT-related issues. |
GDPR Online Test
IT Specialist skills FAQs
What technical skills should IT specialists have?
IT specialists should be proficient in areas like network management, system administration, and cybersecurity. Knowledge of cloud computing and data management is also important.
How can recruiters assess problem-solving skills in IT candidates?
Recruiters can assess problem-solving skills by presenting candidates with real-world IT scenarios during interviews or tests, asking them to outline their approach and solution.
What are the key project management skills for IT specialists?
IT specialists should be able to plan, execute, and manage projects effectively. Skills include setting timelines, managing resources, and ensuring projects meet their goals.
Why are communication skills important for IT specialists?
Communication skills are key for IT specialists to explain technical information clearly to non-technical stakeholders and to collaborate effectively with team members.
How important is continuous learning for IT specialists?
Continuous learning is critical in IT due to rapid technological advancements. IT specialists must stay updated with the latest technologies and industry trends.
What should IT specialists know about regulatory compliance?
IT specialists need to understand relevant laws and regulations to ensure that their company's technology practices and data handling meet compliance standards.
How can IT specialists improve their vendor management skills?
Improving vendor management involves understanding contract terms, building strong relationships with suppliers, and effectively negotiating terms and conditions.
What role does adaptability play in the IT specialist's job?
Adaptability is important for IT specialists as they often need to adjust to new technologies, changing project requirements, and evolving industry landscapes.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



