HTML developers are the backbone of web content, ensuring that the structure and layout of web pages are both functional and visually appealing. They work closely with designers and back-end developers to create a cohesive and engaging user experience.
The skills required for an HTML developer go beyond just knowing HTML. They need to be proficient in CSS for styling, have a basic understanding of JavaScript for interactivity, and possess strong attention to detail. Additionally, problem-solving abilities and effective communication are key to their success.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job HTML Developer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential HTML Developer skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
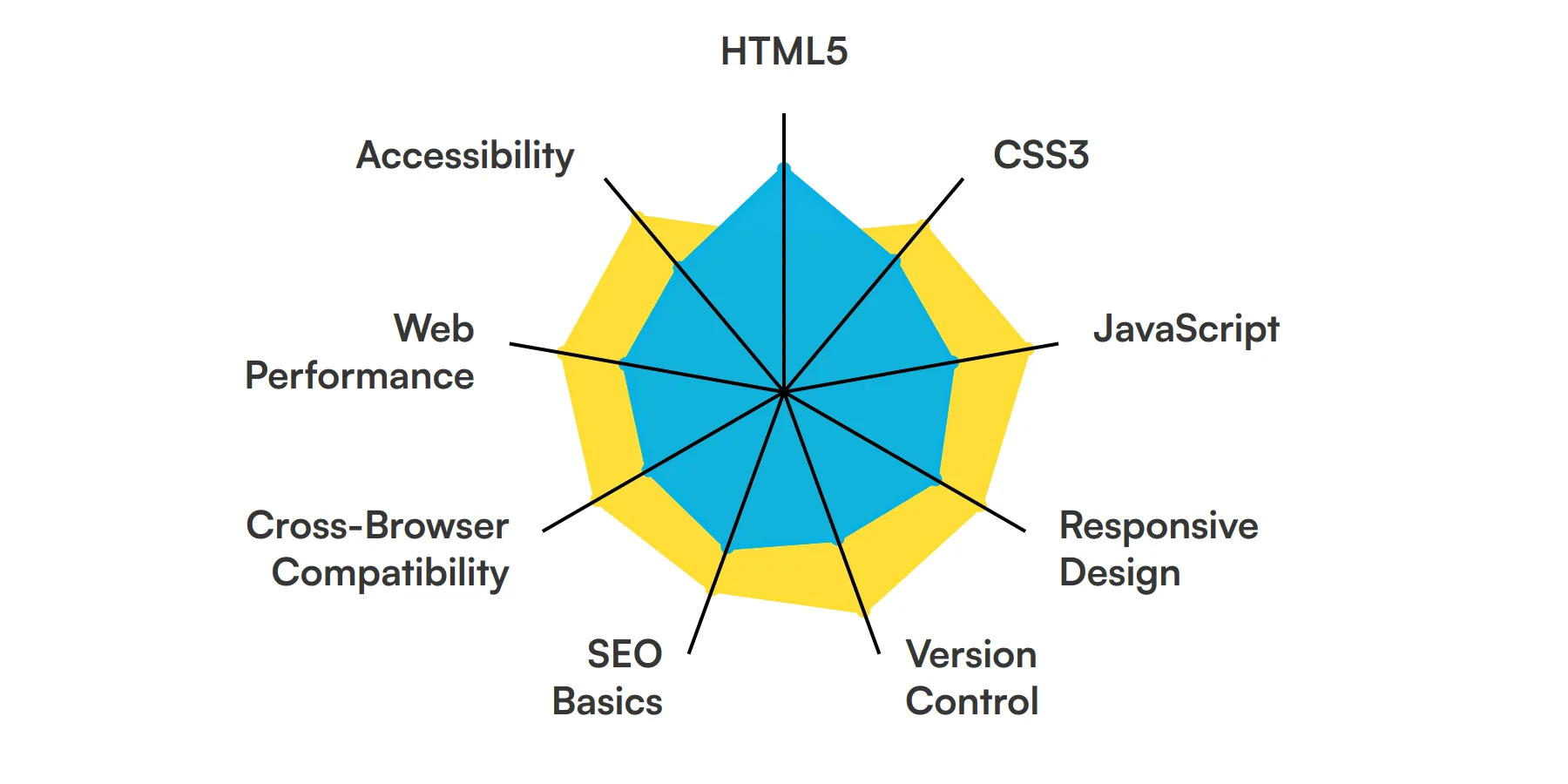
9 fundamental HTML Developer skills and traits
The best skills for HTML Developers include HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, Responsive Design, Version Control, SEO Basics, Cross-Browser Compatibility, Web Performance and Accessibility.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a HTML Developer.
HTML5
HTML5 is the latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language, which structures web content. An HTML Developer uses HTML5 to create and organize web pages, ensuring they are accessible and well-structured for both users and search engines.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a HTML5 Developer Job Description.
CSS3
CSS3 is used to style and layout web pages. An HTML Developer leverages CSS3 to enhance the visual appeal of websites, making them more engaging and user-friendly. This includes everything from fonts and colors to complex animations and responsive designs.
JavaScript
JavaScript is a scripting language that enables interactive web features. HTML Developers use JavaScript to add dynamic elements like sliders, form validations, and interactive maps, enhancing the user experience.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Responsive Design
Responsive Design ensures that web pages look good on all devices, from desktops to smartphones. An HTML Developer must be adept at creating layouts that adapt to different screen sizes, providing a seamless user experience.
Version Control
Version Control systems like Git help manage changes to the codebase. HTML Developers use these tools to collaborate with team members, track revisions, and maintain a history of their work, ensuring smooth project management.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Devops Engineer Job Description.
SEO Basics
Understanding SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is crucial for making web pages discoverable. HTML Developers incorporate SEO best practices in their code to improve the site's visibility on search engines, driving more organic traffic.
Cross-Browser Compatibility
Cross-Browser Compatibility ensures that web pages function correctly across different web browsers. HTML Developers test and optimize their code to provide a consistent experience for all users, regardless of their browser choice.
Web Performance
Web Performance focuses on the speed and efficiency of web pages. HTML Developers optimize images, minify code, and leverage caching to ensure fast load times, improving the overall user experience.
Accessibility
Accessibility involves making web content usable for people with disabilities. HTML Developers follow accessibility guidelines to ensure their websites are inclusive, providing equal access to all users.
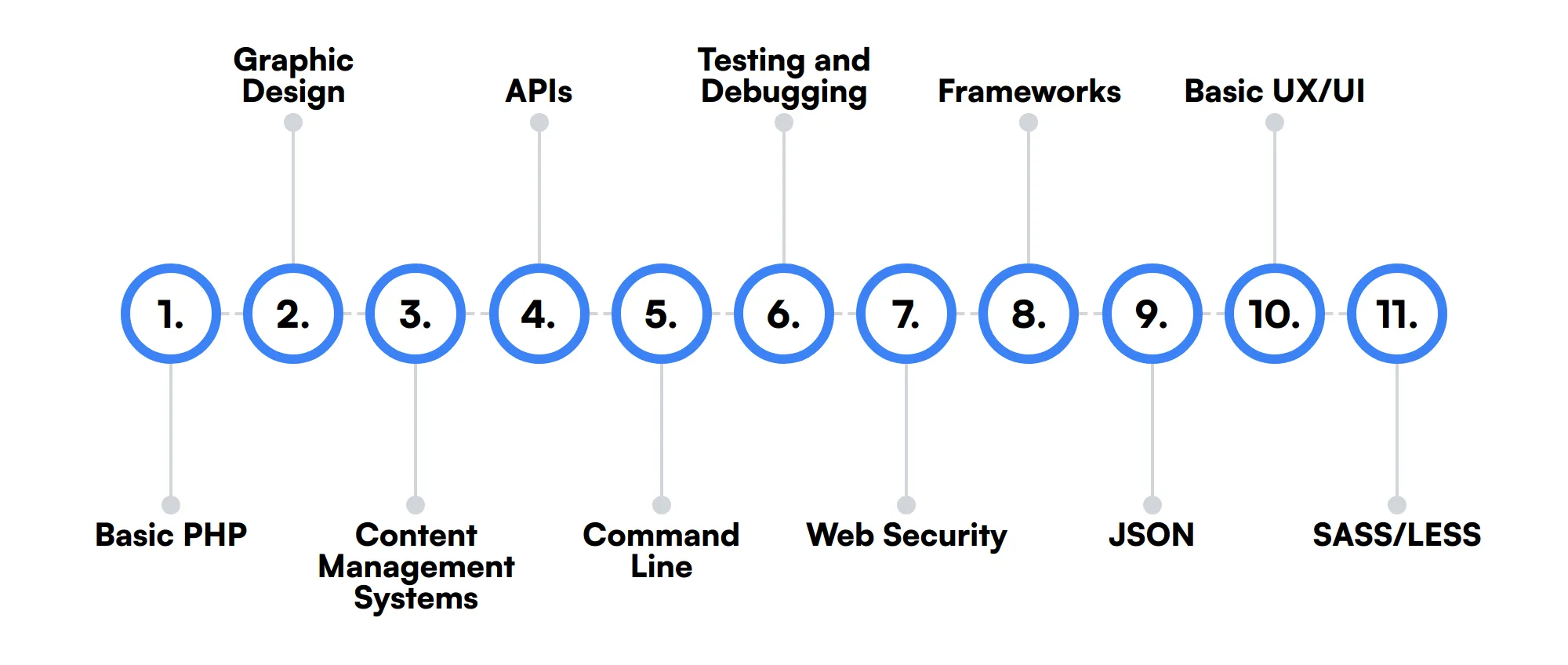
11 secondary HTML Developer skills and traits
The best skills for HTML Developers include Basic PHP, Graphic Design, Content Management Systems, APIs, Command Line, Testing and Debugging, Web Security, Frameworks, JSON, Basic UX/UI and SASS/LESS.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a HTML Developer.
Basic PHP
Basic PHP knowledge allows HTML Developers to understand server-side scripting, enabling them to work more effectively with backend developers and integrate dynamic content into web pages.
Graphic Design
Graphic Design skills help HTML Developers create visually appealing web pages. Understanding design principles like color theory, typography, and layout can significantly enhance the user experience.
Content Management Systems
Familiarity with Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress or Joomla allows HTML Developers to build and manage websites more efficiently, leveraging pre-built themes and plugins.
APIs
Knowledge of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) enables HTML Developers to integrate third-party services into their websites, such as social media feeds, payment gateways, or data from other applications.
Command Line
Using the Command Line can streamline many development tasks. HTML Developers who are comfortable with command-line tools can automate workflows, manage files, and deploy code more efficiently.
Testing and Debugging
Testing and Debugging skills are essential for identifying and fixing issues in the code. HTML Developers use various tools and techniques to ensure their web pages are error-free and function as intended.
Web Security
Understanding Web Security principles helps HTML Developers protect their websites from common threats like SQL injection, XSS, and CSRF. Implementing security best practices is crucial for safeguarding user data.
Frameworks
Familiarity with frameworks like Bootstrap or Foundation can speed up the development process. HTML Developers use these frameworks to create responsive, mobile-first web pages with pre-designed components.
JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. HTML Developers often work with JSON to handle data from APIs, making it easier to integrate and manipulate data within web applications.
Basic UX/UI
Basic UX/UI knowledge helps HTML Developers create user-friendly interfaces. Understanding user experience and interface design principles ensures that web pages are intuitive and easy to navigate.
SASS/LESS
SASS and LESS are CSS preprocessors that extend CSS with variables, nested rules, and functions. HTML Developers use these tools to write more maintainable and scalable stylesheets.
How to assess HTML Developer skills and traits
When hiring HTML developers, it's important to assess not just their knowledge of HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript, but also their ability to create responsive designs, manage version control, and ensure web performance. Finding the right candidate involves looking beyond their resume to understand their practical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Traditional interviews and resume screenings might not fully reveal a candidate's proficiency in areas like SEO basics, cross-browser compatibility, and accessibility. This is where practical assessments come into play. By using skills assessments, you can directly test candidates on the tasks they will face in their daily work.
Adaface assessments offer a tailored approach to evaluate the specific skills of HTML developers. By incorporating real-world problems that require knowledge of essential HTML developer skills, these tests ensure that your candidates are well-equipped to handle the demands of the role. With Adaface, you can improve the quality of your hires and significantly cut down on screening time.
Let’s look at how to assess HTML Developer skills with these 4 talent assessments.
HTML/ CSS Online Test
Our HTML/ CSS Online Test evaluates a candidate's ability to create web pages and style them using CSS.
The test assesses their understanding of core HTML tags, handling forms, and critical CSS concepts like the box model, positioning, and Flexbox. It also includes simple coding questions to evaluate hands-on programming knowledge.
Successful candidates have an expert understanding of CSS layout techniques, responsiveness, and browser compatibility.
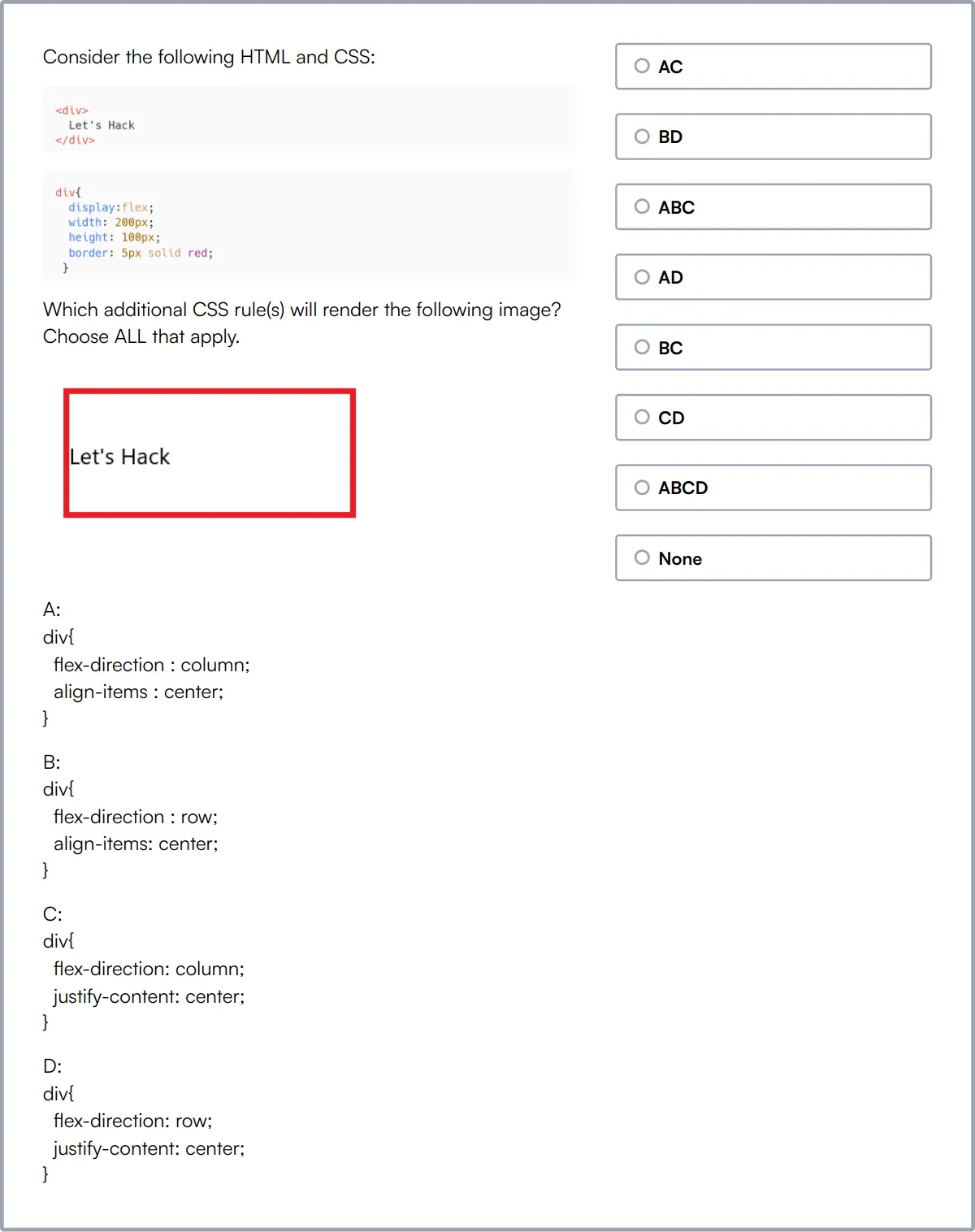
JavaScript Online Test
Our JavaScript Online Test gauges a vital front end dev skill.
The test challenges a candidate’s knowledge of JavaScript basics, ES6 features, and their ability to manipulate the HTML DOM. It also includes coding questions to evaluate hands-on JavaScript programming skills.
We offer a selection of JavaScript tests, including debugging and data structuring, so you can gauge various skill levels.
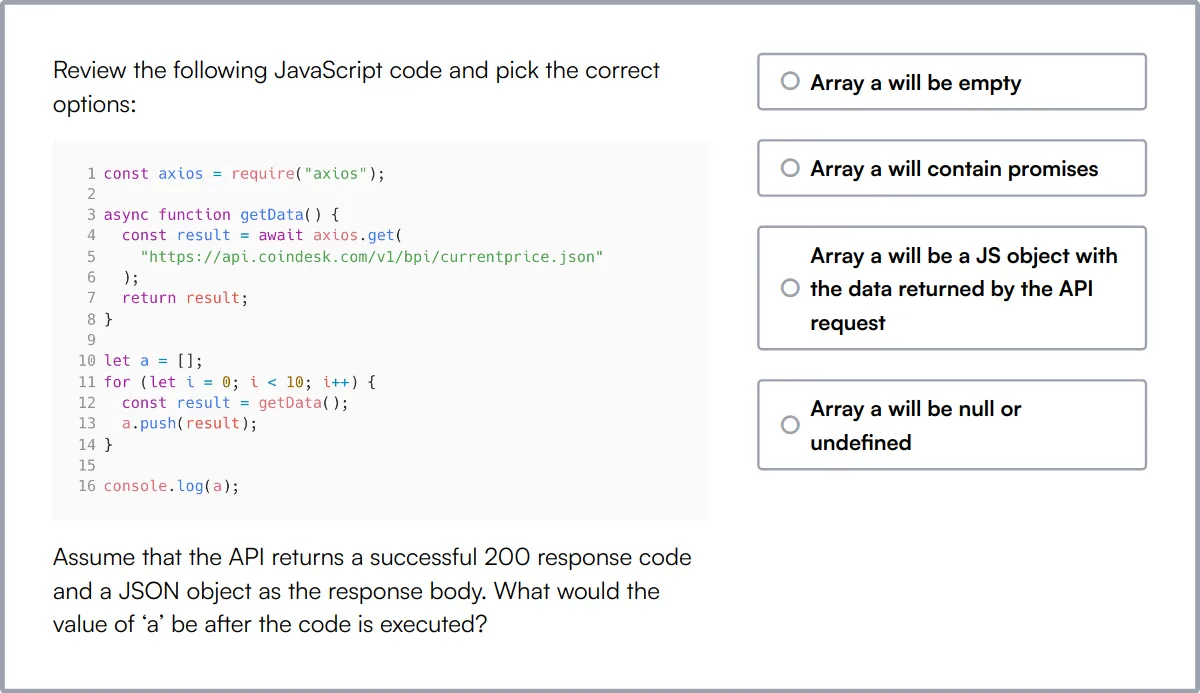
Git Online Test
Our Git Online Test evaluates candidates on their understanding of Git, a popular version control system.
The test assesses their knowledge of basic and advanced Git commands, conflict resolution, and proficiency in using Git to manage source code.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate a strong grasp of Git workflows and branching models.
Web Testing
Our Web Testing Online Test focuses on evaluating candidates' knowledge and skills in Web Testing.
The test includes questions on Web Testing fundamentals, using QA tools like Selenium, and manual testing basics.
Candidates who perform well demonstrate a solid understanding of designing tests and QA engineering principles.
Summary: The 9 key HTML Developer skills and how to test for them
| HTML Developer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. HTML5 | Evaluate developer's ability to structure semantic, interactive web pages. |
| 2. CSS3 | Assess proficiency in styling, layout adaptations, and design aesthetics. |
| 3. JavaScript | Assess a developer’s skills in creating interactive, dynamic designs. |
| 4. Responsive Design | Determine skills in building designs that function across various devices. |
| 5. Version Control | Check usage of tools like Git to manage code changes. |
| 6. SEO Basics | Review understanding of optimizing websites for search engine ranking. |
| 7. Cross-Browser Compatibility | Test ability to ensure consistent look and functionality across browsers. |
| 8. Web Performance | Evaluate techniques for improving site speed and efficiency. |
| 9. Accessibility | Assess knowledge of web standards for accessible design. |
HTML/ CSS Online Test
HTML Developer skills FAQs
What are the key skills to look for in an HTML Developer?
Key skills include HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, Responsive Design, Version Control, SEO Basics, and Cross-Browser Compatibility.
How can I assess an HTML Developer's proficiency in HTML5?
Ask candidates to create a simple webpage using HTML5 elements like <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section>. Review their code for proper structure and semantics.
Why is knowledge of CSS3 important for an HTML Developer?
CSS3 is essential for styling and layout. It allows developers to create visually appealing and responsive designs, which are crucial for user experience.
What is the significance of Responsive Design in web development?
Responsive Design ensures that websites work well on various devices and screen sizes. It improves accessibility and user experience across different platforms.
How do you evaluate an HTML Developer's understanding of SEO Basics?
Check if they use semantic HTML tags, proper meta tags, and alt attributes for images. These practices improve search engine visibility.
What tools can be used to test Cross-Browser Compatibility?
Tools like BrowserStack, CrossBrowserTesting, and LambdaTest can help ensure that websites function correctly across different browsers.
Why is Version Control important for HTML Developers?
Version Control, like Git, helps manage code changes, collaborate with team members, and track project history. It is essential for teamwork and project management.
How can you assess an HTML Developer's skills in Web Performance?
Ask them to optimize a webpage for speed. Look for techniques like minifying CSS/JS, optimizing images, and using lazy loading.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



