Application Engineers are the backbone of software development teams, responsible for designing, developing, and maintaining software applications. They work closely with other engineers, designers, and stakeholders to ensure that applications meet user needs and business goals.
Skills required for an Application Engineer include proficiency in programming languages such as Java, Python, or C++, as well as strong analytical and problem-solving abilities. Additionally, effective communication and teamwork skills are essential for collaborating with cross-functional teams.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Application Engineer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 8 essential Application Engineer skills, 9 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
8 fundamental Application Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Application Engineers include Technical Proficiency, Problem Solving, Programming Skills, System Integration, Client Interaction, Project Management, Quality Assurance and Documentation Skills.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 8 essential skills of a Application Engineer.
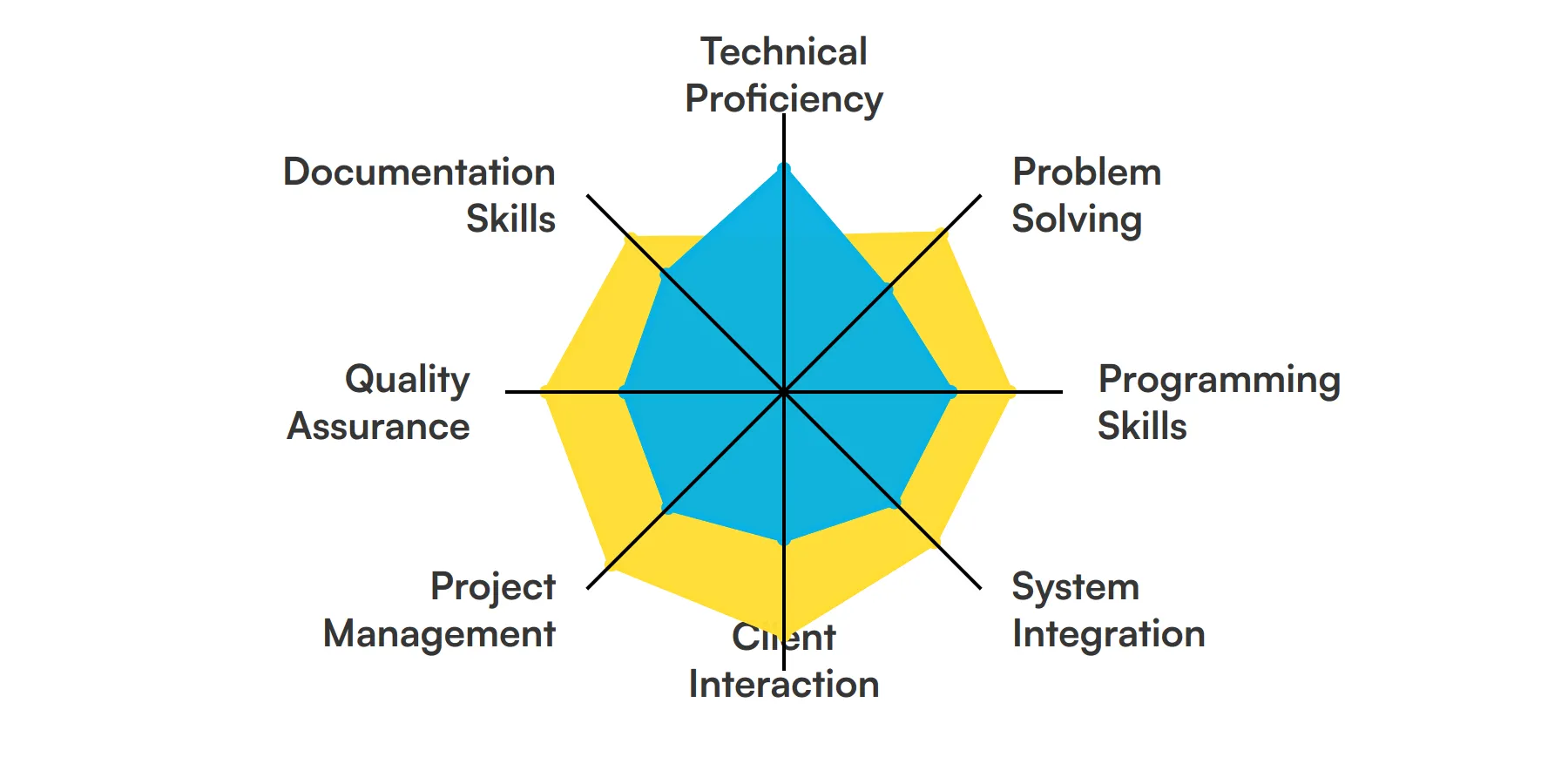
Technical Proficiency
Application Engineers must have a deep understanding of software and hardware systems. This knowledge allows them to design, implement, and troubleshoot applications effectively, ensuring they meet user needs and system specifications.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Application Engineer Job Description.
Problem Solving
In the role of an Application Engineer, the ability to identify and resolve complex technical issues is crucial. They use analytical skills to diagnose problems and devise viable solutions, often under tight deadlines.
Programming Skills
Proficiency in programming languages such as Java, Python, or C++ is essential for Application Engineers. They use these skills to write and test code, develop applications, and integrate systems.
System Integration
Application Engineers need to integrate various hardware and software components into a cohesive system. This skill ensures that all parts work together seamlessly, optimizing the performance and functionality of the application.
Client Interaction
Effective communication with clients is key for Application Engineers to understand project requirements and deliver tailored solutions. They must translate technical details into understandable language for clients and stakeholders.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Project Management
Managing timelines, resources, and project deliverables is a regular duty for Application Engineers. They ensure projects stay on track and within budget, coordinating with different teams to meet project milestones.
Quality Assurance
Ensuring that applications function as intended without bugs is critical. Application Engineers conduct rigorous testing and debugging to uphold software quality and reliability before deployment.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Quality Assurance (QA) Engineer Job Description.
Documentation Skills
Creating clear and detailed documentation is necessary for Application Engineers. This documentation serves as a vital reference for maintenance, upgrades, and compliance with industry standards.
9 secondary Application Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Application Engineers include Version Control, Database Management, Security Practices, Networking Basics, Cloud Technologies, User Interface Design, Performance Tuning, Compliance Knowledge and Continuous Learning.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 secondary skills of a Application Engineer.
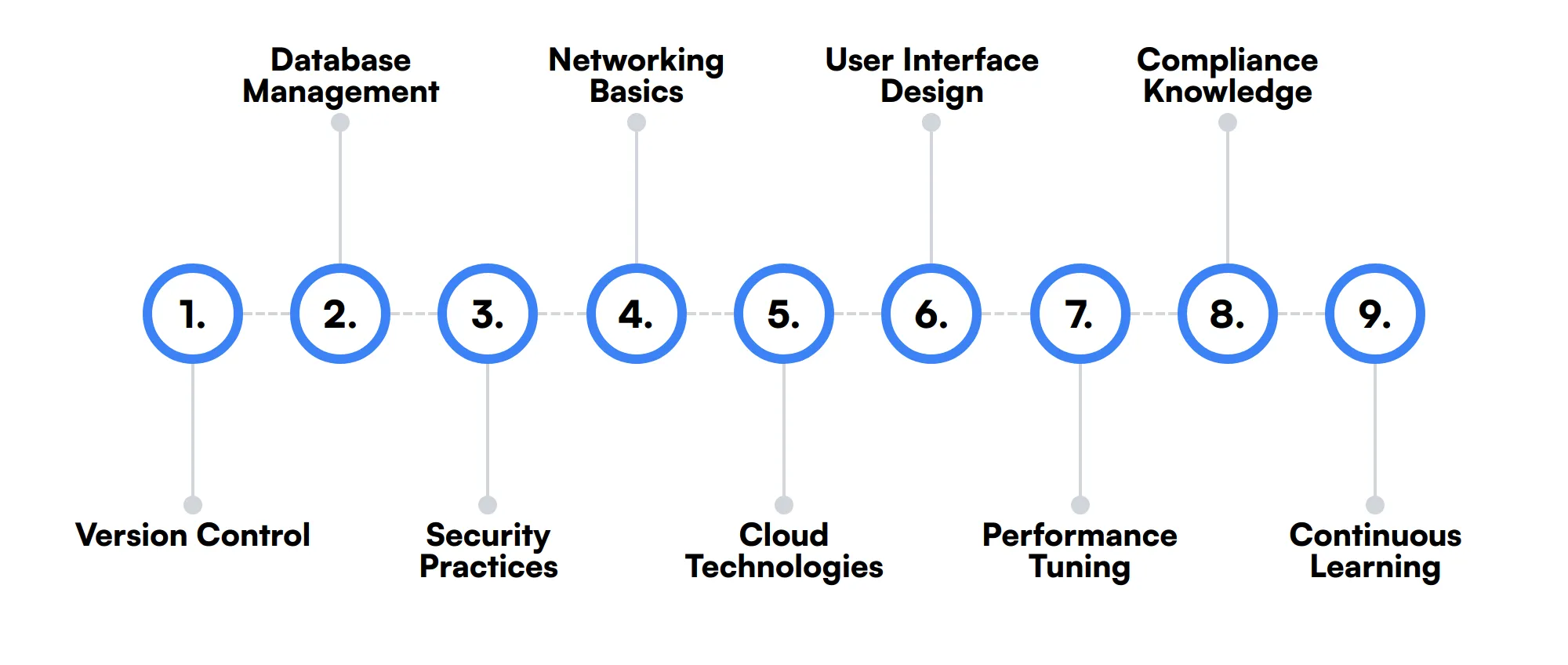
Version Control
Familiarity with version control tools like Git helps Application Engineers manage changes to project codebases, enhancing collaboration and tracking revisions.
Database Management
Understanding database technologies and the ability to manage data effectively is important for Application Engineers when applications involve data manipulation and storage.
Security Practices
Application Engineers must implement security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, ensuring the integrity and safety of the applications.
Networking Basics
A solid grasp of networking principles helps Application Engineers in setting up, managing, and troubleshooting network-related issues within applications.
Cloud Technologies
Knowledge of cloud services and platforms enables Application Engineers to deploy scalable and flexible application solutions, often reducing costs and improving efficiency.
User Interface Design
Skills in UI design are beneficial for Application Engineers to ensure applications are not only functional but also user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing.
Performance Tuning
Application Engineers optimize application performance by identifying bottlenecks and implementing improvements to enhance speed and responsiveness.
Compliance Knowledge
Awareness of relevant legal and regulatory requirements is necessary for Application Engineers to ensure that applications comply with all applicable standards.
Continuous Learning
The tech field is ever-evolving, and staying updated with the latest technologies and methodologies is crucial for Application Engineers to maintain and enhance their skill set.
How to assess Application Engineer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of an Application Engineer can be a multifaceted process. It's not just about verifying technical proficiency or programming skills; it's also about understanding their problem-solving abilities, system integration expertise, and how well they interact with clients. Each of these aspects plays a significant role in determining whether a candidate is the right fit for your team.
Traditional resumes and interviews often fall short in providing a complete picture of a candidate's capabilities. This is where skills-based assessments come into play. By leveraging tools like Adaface on-the-job skill tests, you can achieve a 2x improved quality of hires and an 85% reduction in screening time. These assessments are designed to evaluate a wide range of skills, from project management and quality assurance to documentation and client interaction, ensuring you find the best match for your needs.
Let’s look at how to assess Application Engineer skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Technical Aptitude Test
The Technical Aptitude Test uses scenario-based multiple-choice questions to evaluate a candidate's general technical aptitude and problem-solving skills.
The test covers topics such as basic computer concepts, programming fundamentals, data structures, time complexity, database management, networking and security, system administration, web development, and software engineering. Candidates are also evaluated on their ability to apply critical thinking, logical reasoning, and analytical skills to solve complex technical problems.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong understanding of programming fundamentals, data structures, and algorithm basics. They also show proficiency in technical aptitude and problem-solving skills.
Problem Solving Test
The Problem Solving Test evaluates a candidate's ability to understand instructions, analyze data, and respond to complex problems or situations.
The questions are designed to get insights into their problem solving, learning agility, and coachability. It covers skills such as abstract reasoning, critical thinking, deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, pattern matching, and spatial reasoning.
High-scoring candidates show strong analytical skills and the ability to think critically and logically. They excel in abstract reasoning and pattern matching, demonstrating their capability to solve complex problems.
Computer Programmer Coding Aptitude Test
The Computer Programmer Coding Aptitude Test uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their ability to solve problems using logic, analytical thinking, and programming concepts.
The test assesses candidates' understanding of topics such as algorithms, data structures, programming paradigms, syntax, and programming logic. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to analyze problems, identify patterns, and develop effective solutions using programming concepts.
Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in programming fundamentals, data structures, and algorithm basics. They also show strong coding skills and technical aptitude.
Oracle SOA Online Test
The Oracle SOA Online Test evaluates candidates' knowledge and skills in Oracle Service-Oriented Architecture and related technologies.
The test covers skills such as process editing, wires, Oracle Mediator, binding components, SOA Suite, artifacts, property inspector, SOA composite application, WSDL, and BPEL schema.
Candidates who perform well demonstrate a strong understanding of Oracle SOA Suite and related technologies. They show proficiency in process editing, Oracle Mediator, and SOA composite applications.
Customer Service Aptitude Test
The Customer Service Aptitude Test evaluates a candidate's skills in customer service, attention to detail, problem-solving, verbal reasoning, numerical reasoning, and logical reasoning.
The test includes questions on customer service, situational judgement, abstract reasoning, verbal reasoning, and English. It assesses candidates' ability to handle customer interactions and solve problems effectively.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate strong customer service skills, attention to detail, and effective communication. They excel in verbal and numerical reasoning, showing their ability to handle complex customer interactions.
Project Management Test
The Project Management Test assesses a candidate's ability to plan projects from conception to implementation, map timelines, assess risks, allocate budgets, and manage stakeholders.
The test covers skills such as cost and budget estimation, situational judgement, understanding of key project roles and stages, designing a project plan, resolving issues and handling changes, managing and controlling resources, stakeholder management, prioritizing tasks in real-time, basics of agile project management and Scrum, basics of traditional (waterfall) project management, risk analysis, and creating and analyzing project reports.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong project management skills, including the ability to design project plans, manage resources, and handle stakeholder interactions. They show proficiency in both agile and traditional project management methodologies.

Summary: The 8 key Application Engineer skills and how to test for them
| Application Engineer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Technical Proficiency | Evaluate understanding of core technologies and tools relevant to the role. |
| 2. Problem Solving | Assess ability to identify issues and develop effective solutions. |
| 3. Programming Skills | Test coding proficiency in relevant programming languages. |
| 4. System Integration | Check capability to integrate various systems and software seamlessly. |
| 5. Client Interaction | Gauge communication skills and ability to understand client needs. |
| 6. Project Management | Evaluate ability to plan, execute, and oversee projects. |
| 7. Quality Assurance | Assess skills in testing and ensuring software quality. |
| 8. Documentation Skills | Check ability to create clear, comprehensive technical documentation. |
Full Stack Developer Test
Application Engineer skills FAQs
What technical proficiency should an Application Engineer have?
An Application Engineer should be proficient in various programming languages, software development tools, and operating systems. They should also be familiar with system integration and database management.
How can problem-solving skills be assessed in an Application Engineer?
Problem-solving skills can be assessed through technical interviews, coding challenges, and scenario-based questions that require the candidate to troubleshoot and resolve issues.
Why are programming skills important for an Application Engineer?
Programming skills are essential for developing, testing, and maintaining software applications. They enable engineers to write efficient code and automate tasks.
What is the role of system integration in an Application Engineer's job?
System integration involves ensuring that different software systems and applications work together seamlessly. This includes integrating APIs, databases, and third-party services.
How important is client interaction for an Application Engineer?
Client interaction is crucial for understanding requirements, providing technical support, and ensuring that the delivered solutions meet client expectations.
What project management skills should an Application Engineer possess?
An Application Engineer should be able to manage timelines, coordinate with team members, and ensure that projects are completed within scope and budget.
How can quality assurance skills be evaluated?
Quality assurance skills can be evaluated through knowledge of testing methodologies, experience with automated testing tools, and the ability to write and execute test cases.
Why is continuous learning important for an Application Engineer?
Continuous learning is important to stay updated with the latest technologies, tools, and best practices in the ever-evolving field of software development.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



